Service Level Agreements (SLAs), Service Level Objectives (SLOs), and Service Level Indicators (SLIs) are fundamental concepts for ensuring the reliability and performance of software systems, application or a service. Understanding these concepts can help influence an organization, team, project to work towards achieving and delivering an high performance and reliable service. The whole concept can looked from a top down or bottom up approach to align a service to achieve the business objective.
From an SRE perspective, SLAs, SLOs, and SLIs form a crucial framework for defining, measuring, and improving service reliability.
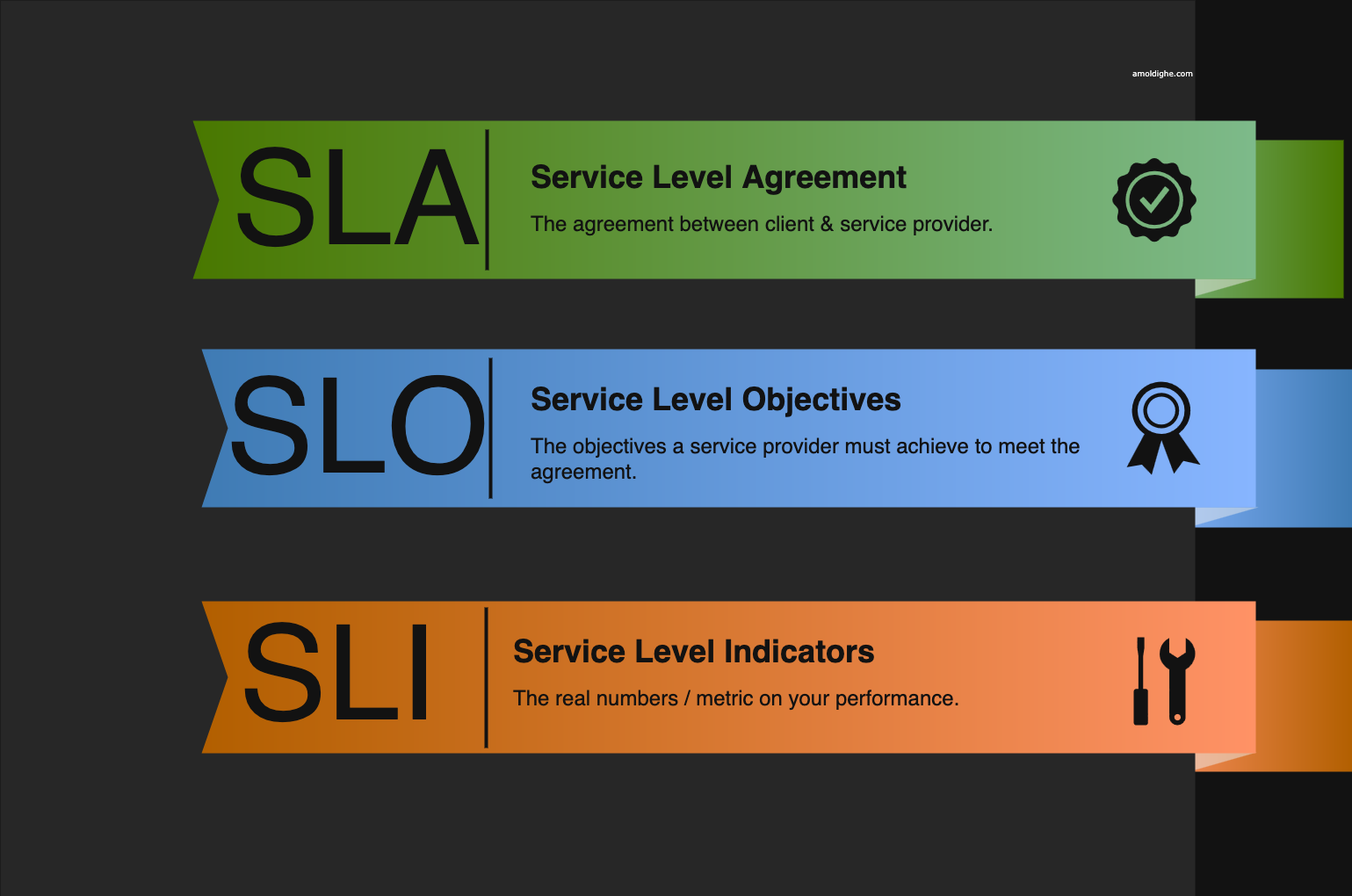
SLA - A formal contract between a service provider and its customers that outlines the agreed-upon service levels. SLAs often incorporate SLOs as a key component. They define the commitments made to customers regarding service performance and availability. SLAs may include penalties for failing to meet agreed-upon SLOs.
SLO - A target for an SLI, expressed as a percentage or other quantifiable measure about specific metrics like uptime, latency, response time. These help the team identify the goal they need to achive to adhear to the SLA. SLOs translate SLIs into concrete goals. They provide a target to strive for, guiding engineering decisions and resource allocation to meet the service objectives. Example: “99.9% of API requests must be served within 200ms.”
SLI - A measurable metric that reflects the performance of a service from a user’s perspective. SLIs are the foundation to define and instrument these metrics to track key aspects like: Availability: Uptime, error rates, latency Performance: Response times, throughput, request success rates Usability: User satisfaction scores, error rates in user interactions